countries with right-hand traffic
The terms right-hand traffic and left-hand traffic refer to regulations requiring all bidirectional traffic to keep either to the right or the left side of the road, respectively.This is so fundamental to traffic flow that it is sometimes referred to as the rule of the road. This basic rule eases traffic flow and reduces the risk of head-on collisions. Though originally most traffic drove on the left worldwide, today about 66.1% of the world's people live in right-hand traffic countries and 33.9% in left-hand traffic countries. About 72% of the world's total road distance carries traffic on the right, and 28% on the left.
Left-hand traffic
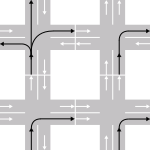
All traffic is generally required to keep left unless overtaking.
Oncoming traffic is seen coming from the right.
Right-turning traffic must cross oncoming traffic.
Most traffic signs facing motorists are on the left side of the road.
Traffic on roundabouts (traffic circles or rotaries) goes clockwise.
Pedestrians crossing a two-way road look first for traffic from their right.
The lane designated for normal driving and turning left is on the left
Most dual carriageway (divided highway) exits are on the left
Other vehicles are overtaken (passed) on the right, though in some circumstances overtaking on the left is permitted.
Most vehicles have the driving seat on the right.
A left turn at a red light may be allowed after stopping.
On roads without a footpath pedestrians may be advised to walk on the right.
Jurisdictions with left-hand traffic
Note: Italics indicates year of change to driving on the left.
* Until late 1960s, imported vehicles from USA were fitted with left-hand drive layout
Total: 76 countries, territories and dependencies
Right-hand traffic
Note: Italics indicates year of change to driving on the right.
*1758 in Copenhagen, 1793 in the rest of Denmark
**In South Yemen
Total: 163 countries and territories



countries with left-hand traffic
The terms right-hand traffic and left-hand traffic refer to regulations requiring all bidirectional traffic to keep either to the right or the left side of the road, respectively.This is so fundamental to traffic flow that it is sometimes referred to as the rule of the road. This basic rule eases traffic flow and reduces the risk of head-on collisions. Though originally most traffic drove on the left worldwide, today about 66.1% of the world's people live in right-hand traffic countries and 33.9% in left-hand traffic countries. About 72% of the world's total road distance carries traffic on the right, and 28% on the left.
Left-hand traffic

Jurisdictions with left-hand traffic
Note: Italics indicates year of change to driving on the left.
| Alderney Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Australia Bahamas Bangladesh Barbados Bermuda Bhutan Botswana Brunei Cayman Islands Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands Cook Islands Cyprus Dominica East Timor (drove on right 1928-1976) Falkland Islands Fiji Grenada Guernsey Guyana Hong Kong India | Indonesia* Ireland Isle of Man Jamaica Japan (Okinawa 1978)Jersey Kenya Kiribati Lesotho Macau Malawi Malaysia Maldives Malta Mauritius Montserrat Mozambique Namibia (1918) Nauru (1918) Nepal New Zealand Niue Norfolk Island Pakistan Papua New Guinea Pitcairn Islands | Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa (2009) Seychelles Singapore Solomon Islands South Africa Sri Lanka Suriname Swaziland Tanzania Thailand Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda United Kingdom British Virgin Islands U.S. Virgin Islands Zambia Zimbabwe |
* Until late 1960s, imported vehicles from USA were fitted with left-hand drive layout
Total: 76 countries, territories and dependencies
Right-hand traffic

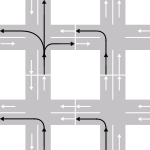
- All traffic is generally required to keep right unless overtaking.
- Oncoming traffic is seen coming from the left.
- Left-turning traffic must cross oncoming traffic.
- Most traffic signs facing motorists are on the right side of the road.
- Traffic on roundabouts (traffic circles or rotaries) goes anticlockwise.
- Pedestrians crossing a two-way road look first for traffic from their left.
- The lane designated for normal driving and turning right is on the right.
- Most dual carriageway (divided highway) exits are on the right
- Other vehicles are generally overtaken (passed) on the left, though in some circumstances overtaking on the right is permitted.
- Most vehicles have the driving seat on the left.
- A right turn at a red light may be allowed after stopping.
- On roads without a footpath pedestrians may be advised to walk on the left.
Note: Italics indicates year of change to driving on the right.
| Afghanistan Albania Algeria American Samoa Andorra Angola (1928) Argentina (1945) Armenia Aruba Austria (1935–38) Azerbaijan Bahrain (1967) Belarus Belgium Belize (1961) Benin Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burma (Myanmar) (1970) Burundi Cambodia Cameroon (1961) Canada (1920s) Cape Verde (1928) Central African Republic Chad Chile China, mainland (1946) Colombia Comoros Congo (Brazzaville) Congo (Kinshasa) Costa Rica Côte d'Ivoire Croatia Cuba Czech Republic (1939, details)Denmark 1793* | Djibouti Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea (1964) Estonia Ethiopia (1964) Faroe Islands Finland (1858) France (1789) French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia (1965) Georgia Germany Ghana (1974) Gibraltar (1929) Greece Greenland Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau (1928) Haiti Honduras Hungary (1941) Iceland (1968) Iran Iraq Israel Italy Jordan Kazakhstan Korea DPR Korea (1946) Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos | Latvia Lebanon Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Republic of Macedonia Madagascar Mali Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mayotte Mexico Micronesia Midway Atoll Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia Nicaragua Niger Nigeria (1972) Northern Mariana Is. Norway Oman Palau Panama (1943) Paraguay (1945) Peru Philippines (1946) Poland Portugal (1928) Puerto Rico Qatar Réunion | Romania Russia Rwanda Saint Pierre and Miquelon San Marino São Tomé and Príncipe (1928) Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Sierra Leone (1971) Slovakia (1939-41) Slovenia Somalia (1968) Spain (October 1924) Sudan (1973) Svalbard Sweden (1967 ) Switzerland Syria Taiwan (1946) Tajikistan Togo Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Ukraine United Arab Emirates United States (1792) Uruguay (1945) Uzbekistan Vanuatu Vatican City Venezuela Vietnam Wake Island Wallis and Futuna Western Sahara Yemen(1977)** |
*1758 in Copenhagen, 1793 in the rest of Denmark
**In South Yemen
Total: 163 countries and territories

World map showing the driving directions for all countries and any changes that have occurred in the past starting with Finland's change in 1858.
Has always driven on the right (RHT).
Originally drove on the left, but now drives on the right.
Has always driven on the left (LHT).
Originally drove on the right, but now drives on the left.
Once had different rules of the road (depending on one's location), but now drives on the right.


No comments:
Post a Comment